Babies Categorized as Very Low Birth Weight Weigh Less Than _____ Pounds.
Click for pdf: Consequences of Prematurity
1. Definition
Prematurity is divers as an underdeveloped newborn child with a low birth weight that is born before 37 weeks of gestation. Other terms used to describe prematurity are: "preterm" and "preemie." Infants having a gestational age of 35 and 37 weeks are termed 'moderately premature,' those built-in betwixt 29 and 34 weeks of gestation are termed 'very premature', and those built-in at 28 weeks of gestation or less are termed 'extremely premature.
two. What Gestational Historic period is Viable?
The survival rate of infant's born between 22 and 31 weeks of gestation increases with each additional week of gestation. The Textbook of Neonatal Resuscitation suggests that non-initiation of resuscitation for newborns less than 23 weeks gestational age and-or 400 grams in birth weight is appropriate. Most babies built-in after about 26 weeks gestation exercise survive to one year, although they may face an extended stay in the NICU.
Improvements of medical engineering science have increased the viable age for infants with a ascension rate of survival for premature infants between 23 – 31 weeks. The following table displays the statistics obtained for the survival of alive inborn babies admitted to NICU from 1995 to 2007.

Survival of live inborn babies admitted to NICU from 1995 to 2007 (due north = 2334) Adapted from National Women's Newborn Services Annual Clinical Report (2007)
Infants can also be categorized by nativity weight. A low birth weight babe weighs less than 2500g, (5 1/two lbs) a very depression nativity weight babe weighs less than 1500g (3 ane/2 lbs) and an extremely low birth weight infant weighs less than 1000g (2 ane/4 lbs) which helps in determining their true gestational age. "Authentic gestational age is critical considering the variation of 1 week in the determined age of an extremely premature infant (25 weeks instead of 24 weeks, for case) produces a far different ready of prognostic implications. The initial complete examination at birth is the all-time way to appraise gestational age accurately. In the early on minutes to hours of the life of the marginally viable babe, much medical information becomes available and—typically—drives the decision-making process. At this point, predictions are made, outcomes are assessed, and a medical program is put in place" [17]. The viability limit differs by age from hospital to infirmary, although very few babies accept survived being born at the gestational age of 22 weeks, viability limits usually fall somewhere between 23 and 35 weeks.
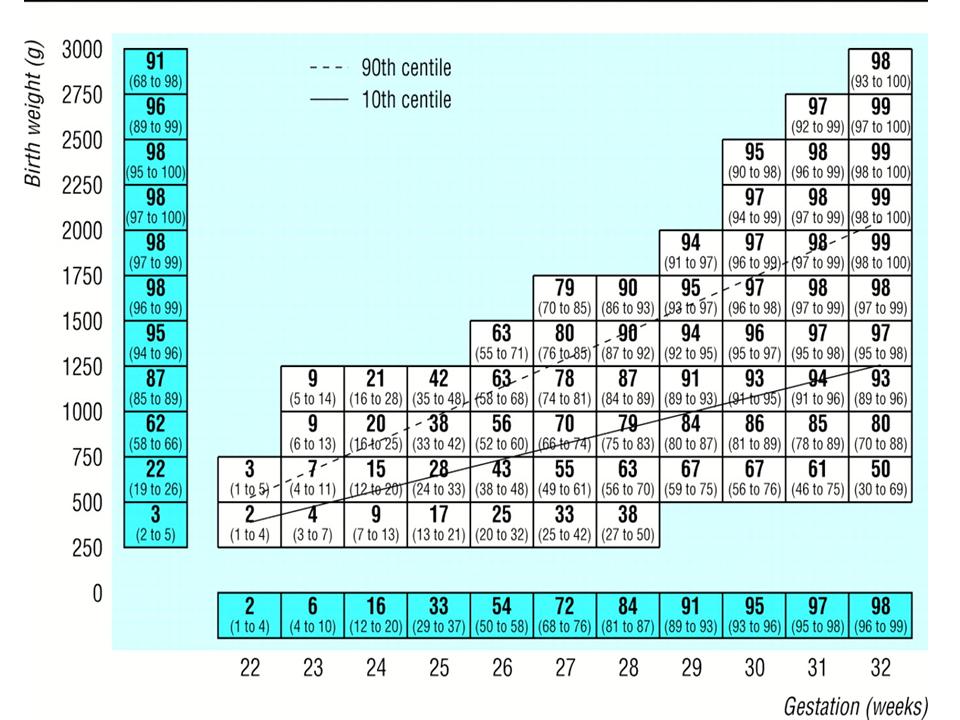
Median (95% confidence interval) predicted percentage survival for European infants known to exist alive at onset of labour. Values above 90th centile represent infants large for gestational age, values below 10th centile represent infants small for gestational age. Adapted from Draper et al. (1999).
3. Presentation
Currently, 12 percentage of all babies are born premature. This has been a rising statistic as multiple births are now more mutual, likely as a effect of in vitro fertilization. Most premature infants are characterized by low birth weight pregnant that they weigh less than 2500 grams (5.five pounds). Premature infants may also be unable to feed by oral fissure, breathe without apneas, or thermo-regulate. As a result of being born prematurely, major organs will not accept had plenty time be fully develop, leading to several premature specific wellness consequences. Although whatsoever premature infant tin can be built-in with wellness risks, infants built-in before 32 weeks are most probable to have astringent health risks.
Possible complications include (see appendix for definition):
Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH)
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
- Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD)
- Anemia of Prematurity
- Neonatal Sepsis and Other Infections
- Built Heart Disease
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyperbilirubinemia
- Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (severe intestinal inflammation)
- Delayed growth and development
4. What causes premature births?
In approximately 40 percent of premature births, the cause is unknown. Still, there are many reasons why a premature birth occurs. Women who have had any of the following are at run a risk of premature births:
- Having previously delivered prematurely
- Premature rupture of the amniotic sac (ruptured membranes)
- Infections of the urinary tract or cervix
- A weak cervix—prior surgical procedures
- Abnormalities in the uterus, including fibroids and malformations of the
- uterus
- Multiple gestation
- Smoking, drinking, or other substance use during pregnancy
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy
- Polyhydramnios (an backlog amount of amniotic fluid)
- Chronic diseases carried past the mother that correlate with premature births include:
- Diabetes
- Heart affliction
- Kidney disease
- Systemic Lupus Erythematous
- High claret pressure level (Pregnancy Induced Hypertension and HELLP Syndrome)
five. What should family physicians exist aware of when seeing these children?
The major medical concerns involving premature infants are the result of nether-development of the major organs and master functions of the human trunk. The following categories, adapted from Sears et al. (2004), describes the signs, symptoms and possible outcomes for infants who are built-in prematurely:
Central Nervous System:
Infants built-in at 32 weeks are highly susceptible to intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH). The upper part of the brain consists of two cerebral hemispheres and within each is a ventricle where cerebralspinal fluid is produced and circulates towards the subarachnoid space. Increased susceptibility results from stressors of other weather condition due to prematurity such as respiratory distress. Fluid from both hemispheres flow toward key and lower parts of the brain through narrow channels, and and so toward and effectually the spinal cord. Blood vessels break in the germinal matrix, which is characterized as a pocket-size region adjacent to the ventricles where new nerve cells are produced. The germinal matrix is more than prominent and frail in smaller, premature infants and dissapears by approximately 34 weeks whereafter bleeding is unlikely.
The extent of IVH is graded co-ordinate to the post-obit table:
| Classification | Prognosis | |
| Grade I | Haemorrhage in the germinal matrix only. (No blood in the ventricles.) | Grade I and II bleeds are reabsorbed and often take no permanent effects. |
| Course II | Bleeding in the germinal matrix and ventricle(s), without enlargement of the ventricle(south). | |
| Grade Three | The quantity of blood in the ventricle(s) is large enough to cause enlargement of the ventricle(due south). | Grade Three bleeds tin can cause deficits due to stretching of the brain that occurs when the ventricles are dilated. |
| G rade IV | Claret in extended areas of the brain beyond the germinal matrix. | Usually associated with permanent effects due to the direct damage of brain tissue by the bleeding; The caste of permanent arrears relates to the size and location of bleeding. |
Adapted from University of Pennsylvania Health Systems (2009)
It is very hard to predict the degree of long-term effects resulting from neonatal brain injury, since about brain development has yet to occur, and pregnant compensation for deficits can take place.
Ventriculoperitoneal shunts
Used in surgery to save pressure inside the skull due to fluid buildup on the brain known as hydrocephalus. This procedure is washed by removing fluid from the brain to another part of the body and should be washed equally presently as hydrocephalus is diagnosed. The procedure is ultimately done to remove excess fluid and reduce pressure in the brain. This procedure involves the use of full general anesthesia. A catheter is placed into one lateral ventricle and attached to a cap and valve positioned below the scalp. Tubing is tunneled subcutaneously from the valve to the abdomen, where it is deposited into the sterile peritoneal cavity for continuous drainage. Shunts typically transfer and drain the CSF from the lateral ventricles of the encephalon and empty the CSF into the correct peritoneal crenel. Every bit with any foreign object placed in the body, infection is potentially a dangerous complication.
Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL)
PVL is the virtually common ischemic brain injury in premature infants. The ischemia occurs in the border zone at the finish of arterial vascular distributions and in the white matter adjacent to the lateral ventricles. The diagnostic hallmarks of PVL are periventricular echodensities or cysts detected by cranial ultrasonography. Diagnosing PVL is of import due to the meaning pct of surviving premature infants with PVL who develop cognitive palsy (CP), intellectual impairment, or visual disturbances.
Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
HIE is characterized as an acute problem with swelling and irritation of the brain caused by lack of oxygen to the brain. In mild cases the baby recovers completely, notwithstanding in more severe cases it tin can result in permanent brain harm. The virtually common cause of neonatal seizures is HIE brain injury. An asphyxial injury may occur in utero equally a result of decreased uteroplacental perfusion, for example in abruptio placenta, cord pinch, preeclampsia, or chorioamnionitis. Postnatally, conditions such equally persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, cyanotic congenital heart disease, sepsis, and meningitis tin can also result in hypoxic-ischemic encephalon injury. In those infants with HIE who have seizures, onset of seizures is by and large inside the kickoff 24 hours subsequently birth. Withal, the timing of onset is non a reliable indicator of the timing of the neurologic injury.
Treatment of neonatal seizures should focus on the main etiology besides as straight seizure control. Phenobarbital is frequently used as the first line anticonvulsant, followed by phenytoin and lorazepam. Oral phenytoin is poorly absorbed from the baby GI tract. Infants who survive astringent encephalopathy are more likely to experience a poor outcome at historic period two years in comparing with infants who recover from moderate encephalopathy (62% vs 25%). Overall, about 40% of infants who feel neonatal encephalopathy exhibit significant developmental filibuster at age 2 years compared with healthy children. Suboptimal head growth occurs in approximately fifty% of infants surviving hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and is associated with white thing injury and basal ganglia and thalamic lesions. Severe hearing impairment is an important long-term consequence, necessitating sequential surveillance through age iii years. Children who have v-minute Apgar scores of 3 or less at nascence and signs of neonatal encephalopathy are at increased take a chance of developing minor motor impairments and seizures. They demonstrate a greater-than-expected demand for educational help during their early on schoolhouse years and show decreased performance in reading, mathematics, and fine-motor skills. Behavioral and emotional issues are also more prevalent.
Pulmonary System:
Delaying nascence gives lung tissue extra time to mature, and improves lung function of premature babies at birth. During the delay before birth, mothers of premature babies may exist prescribed steroids. "Steroids (glucocorticoids) tin speed the development of a preterm infant's lungs betwixt 24 and 34 weeks gestation, and are often administered during preterm labor" [vi]. Steroids help promote the production of surfactant, a substance that fetus' lungs commencement making at around 26 to 34 weeks of pregnancy, coats the insides of the lungs and keeps them open so they tin can breathe in air after nascence; Ultimately, surfactant prevents the plummet of alveoli (small sacs in the lungs where air is exchanged).
The timing of the dose of steroids is of import. Steroids must be given to the female parent equally an injection several hours before the babe is delivered. A second dose is usually given 24 hours after the first dose. There is probably some benefit from steroids, even if the woman delivers earlier the second dose is given. The greatest do good is seen when the steroid is given at least 48 hours before the infant is delivered [6]. Currently, the nigh commonly used steroid is betamethasone, used to decrease the infant's risk for intraventricular hemorrhage (bleeding into the brain), complications affecting the bowels, circulatory system and a common condition known as respiratory distress syndrome (RDS).
RDS occurs when the infants lungs are not developed enough to make surfactant. The baby then has to piece of work hard to breathe. Signs and symptoms that are seen with RDS include:
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Sharp pulling on the breast beneath the ribs with each jiff taken in.
- Grunting sounds during exhalation
- Flaring of the nostrils during breathing.
Bogus breathing devices and surfactant tin be used to treat this syndrome, however, depending on how severe the RDS is, these babies may develop other serious medical bug that include:
- A collapsed lung
- Leakage of air from the lung into the breast cavity
- Broncopulmonary dysplasia (BDP)
- Intraventricular hemmorage (IVH)
- Sepsis
- Bleeding in the lungs
- Kidney failure
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
Another common weather condition regarding the pulmonary organisation of the premature kid is known as broncho-pulmonary dysplasia (BPD). This is a chronic lung illness acquired by high levels of oxygen for long periods of time or with prolonged treatment of respiratory distress syndrome using a ventilator. Long term consequences consist of chronic lung diseases such every bit asthma and cystic fibrosis. Further, many become very susceptible to respiratory infections such every bit influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), pulmonary edema and pneumonia.
Children who accept a history of BPD may develop rare complications that tin occur with the ciruculatory system resulting in pulmonary hypertension. Overall, the effects of BPD tin play a significant role in regards to increased chest infections and decreased exercise tolerance. Medications needed to inhibit the effects of BPD tin even result in undesired furnishings such as dehydration and low sodium levels from diuretics; kidney stones, hearing problems and low potassium and calcium levels from long term utilize of furosemide.
Cardiovascular System:
The center in fully developed infants has a ductus arteriosus (DA) that allows proper uptake of oxygen through the umbilical cord. With the infant'southward first breath, this ductus arteriosis constricts to allow the pulmonary circulation to take over. Premature infants can be critically under-developed which can effect in patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), which causes abnormal blood menstruum between the aorta and pulmonary avenue, leading to center failure.
In normal birth weight and full-term neonates, the DA closes within 3 days after birth. However, the DA is patent for more 3 days after nativity in eighty% of preterm neonates weighing less than 750 grand and its persistent patency is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Furthermore, in the presence of a pregnant left-to-right ductal shunt in low nascence weight (LBW) neonates, a decreased peripheral perfusion and oxygen delivery occurs. At birth, expansion of the neonatal lungs is associated with an immediate fall in pulmonary vascular resistance. In neonates, a middle murmur is discovered within the get-go few days or weeks of life. The murmur is usually recognized every bit systolic rather than continuous in the start weeks of life and can mimic a benign systolic murmur [12].
A hyper dynamic, precordial impulse, total pulses, widened pulse pressure, hepatomegaly, and a high parasternal systolic murmur have been described as the classical physical signs of PDA. They usually announced almost day 5 onwards and, together with evidence of interrupted improvement of worsening respiratory status, have been established as the clinical criteria of heamodynamic significance [5].
Gastrointestinal System:
Premature infants lack the full ability to obtain nutritional needs from the placenta via the umbilical string. They do not have fully developed digestive systems and are incapable of properly processing food. As a consequence, newborn premature infants are highly susceptible to inflammation of the lining of the intestines besides as many other possible infections including necrotizing enterocolitis – which results in bowel obstruction or tissue death.
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
NEC is the most common gastrointestinal disorder of premature infants. Despite affecting thousands of neonates in the Usa alone, the etiology of NEC is unknown and no effective preventative treatments exists. Development of NEC is likely multifactorial, with prematurity, enteral formula feeding, intestinal hypoxia/ischemia and bacterial colonization being the major take a chance factors [7].
NEC typically occurs inside the fist 2 weeks of life and involves many signs and symptoms that may include:
- poor tolerance to feedings
- feedings stay in stomach longer than expected
- decreased bowel sounds
- abdominal distension (bloating) and tenderness
- greenish (bile-colored) vomit
- redness of the abdomen
- increment in stools, or lack of stools
- encarmine stools
- apnea
- bradycardia
- diarrhea
- lethargy
- fluctuating body temperature.
- advanced cases may show fluid in the peritoneal cavity, peritonitis, or shock.
Diagnosis of NEC can be confimred by the prescence of an abnormal gas design every bit seen on an 10-ray. Characterized by a "bubbly" appearance of gas in the walls of the intestine ("pneumatosis intestinalis", large veins of the liver, or the presence of air outside of the intestines in the abdominal cavity.
Treatment of NEC includes:
- stopping feeds
- nasogastric drainage
- intravenous fluids or fluid replacement and nutrition
- frequent examinations and X-rays of the belly
Eyes:
Retinopathy is common in premature infants due to the under-evolution of the blood vessels to the retina. As a effect, Retinopathy of Prematurity (when the vessels stop growing or grow abnormally causing bleeding in the eye) can occur in most premature infants. Severe cases tin can result in vision loss, merely in some cases can be treated with surgery, laser therapy or may resolve naturally over fourth dimension.
The American University of Pediatrics, the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, and the American Academy of Ophthalmology released a joint argument recommending that initial screening examinations be performed between 4 and 6 weeks of chronological age or 31 and 33 weeks of postconceptional age.
Hearing:
The probability that a baby will suffer from some sort of hearing deficit increases with the caste of prematurity. Total development of the ear (ear pulsate, eustachian tube etc.) does not fully mature until as belatedly as the 26th week of pregnancy. As a result, hearing loss in premature infants tin can be due to injury, infection or a congenital defect.
It is extremely important to assess hearing before infants get out the NICU and to follow upwards for several months afterward. Without consistent follow up to assess hearing, premature babies can feel a great disadvantage in learning and development. Missed diagnosis of hearing bug can result in significantly worsened symptoms. Ultimately, whether handling is successful or not, information technology is e'er meliorate to know that the trouble exists so that other steps to improve their life and learning tin can be taken. Types of hearing problems include:
Sensorineural hearing loss
Originates in the inner ear and is frequently due to prenatal infections, asphyxia either during or soon afterward birth, or genetic factors. Under usual circumstances, sensorineural hearing loss cannot be reverssed medically or surgically. Hearing aid are often administered to minimize the effect of the condition.
Conduction hearing loss
Originates in the heart or outer ear and is caused by obstructions such every bit wax, fluid or a rupture and/or puncture of the ear drum inhibiting audio from being conducted to the inner ear. Conduction hearing loss can usually exist treated medically or surgically.
Growth and Development:
To empathise the growth of a premature infant, it is important to recognize the growing progress of a full term infant. Virtually healthy full term infants proceeds weight co-ordinate to the following tabular array:
| Age | Weight gain per twenty-four hour period | Weight gain per month |
| One to iii months | xxx 1000 | 900 g |
| Four to 12 months | twenty k | 600 g |
Adjusted from Landsdown and Walker (1996)
On average, full term newborn babies double their birth weight by four months and triple it by one yr of historic period. The following growth charts, adjusted from the World Health Organization (WHO), is useful to compare the progress of the premature baby to a full-term baby.
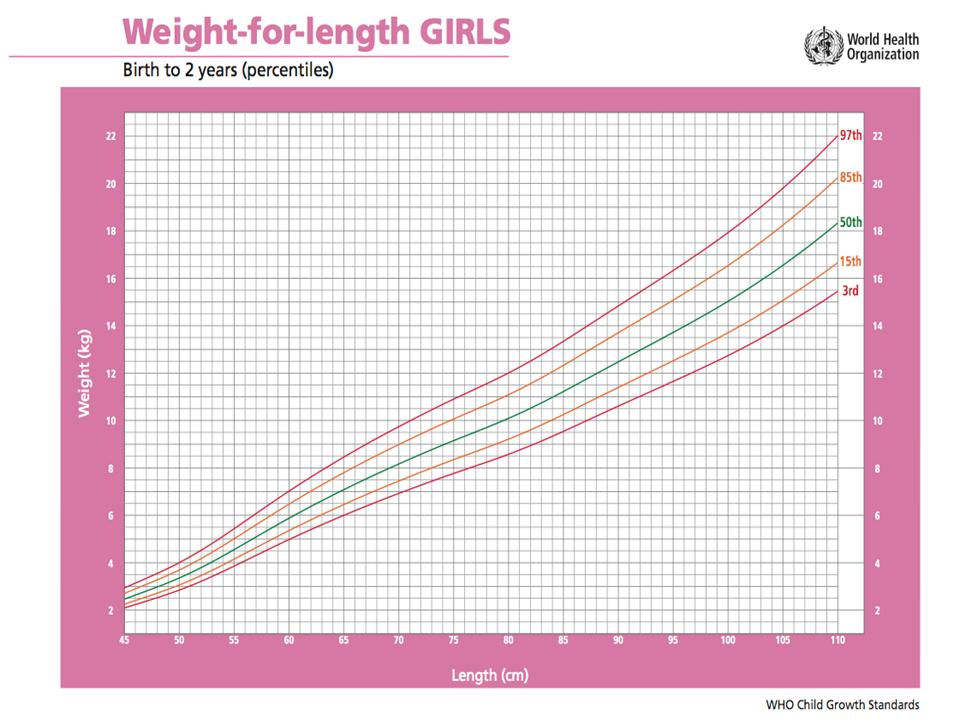

Many infants, built-in pre-term or total-term, grow and gain weight at different rates. If inadequate rate of growth becomes prominent using the standard growth chart, it could mean there is a problem such as "failure to thrive".
Failure to thrive:
- weight less than the third percentile on a standard growth chart
- weight 20% beneath the platonic weight for height
- fall off from a previously established growth curve.
It is of import to carefully assess babies who are declining to thrive and to diagnose a crusade for growth failure. Peadiatricians or family doctors must pay particularly close attention to babies experiencing failure to thrive and to follow up on a consistent ground to diagnose the status.
Encephalon growth can be dictated by head circumference. Measurements are fabricated at the largest surface area of the head, above the eyebrows and ears, and around the dorsum of the caput. Meausurements obtained should be compared with normal ranges for babies of the same age. Signs to be enlightened of are an unusually big head which may infer an increased amount of fluid within the skull. A smaller head size may indicate under-development of the brain.
half-dozen. What happens to children who survive?
Premature children who survive by the first year of life volition take decreased bloodshed rates compared to full term children. Research done by Swamy et al (2008) found that sixty percent of babies born at 26 weeks of gestation take long-term disabilities that include chronic lung illness, deafness, blindness and neurodevelopment issues. Infants born at 31 weeks were found to be xxx per centum less susceptible to these atmospheric condition.
Swamy et al. (2008) found that premature children who survive into adolescence continue to demonstrate consequences of their early entry into life. Males born between 22 and 27 weeks were 76 percentage less likely to reproduce, whereas women born during the same gestational period were 67 percent less probable to have children. Research also revealed that women who are born prematurely are at much higher hazard of giving nativity to preterm offspring as well, however, the study revealed men showing no signs of premature successors.

Adapted from Wood et al. (2000).
7. Conclusion
Most premature infants exhibit long term effects of wellness risks in which many of the medical problems encountered as a result of a premature birth continue into babyhood and can remain over the lifespan. Current evidence has found that the more premature an infant, the smaller the birth weight. Although research has provided evidence of long term increased wellness risks, it is of import to keep in mind that the consequences of prematurity vary with each individual. It is our role as physicians to know the health risks that back-trail prematurity and follow patients accordingly.
8. Appendix
Anemia of Prematurity – Infants born prematurely develop the anemia of prematurity (AOP), associated with the earlier onset of a more than pronounced anemia that is inversely proportional to the gestational age at nascence. typically occurs at 3 to 12 weeks after birth in infants less than 32 weeks gestation and resolves spontaneously by iii to six months. Many infants are asymptomatic despite having very depression concentrations of hemoglobin. Other infants with AOP are symptomatic with tachycardia, poor weight gain, increased requirement of supplemental oxygen, or increased episodes of apnea or bradycardia.
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) – a chronic lung disorder that is most common amid children who were born prematurely, with low birthweights and who received prolonged mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory distress syndrome. BPD is clinically defined as oxygen dependence to 21 post-natal days. BPD is characterized past inflammation and scarring in the lungs. More specifically, the high pressures of oxygen commitment result in necrotizing bronchiolitis and alveolar septal injury, further compromising oxygenation of claret.
Eye Disease – Any disorder that affects the centre. Sometimes the term "heart disease" is used narrowly and incorrectly equally a synonym for coronary artery disease. Heart affliction is synonymous with cardiac affliction only not with cardiovascular disease which is any disease of the heart or blood vessels.
Hyperbilirubinemia – An elevated level of the pigment bilirubin in the blood. A sufficient summit volition produce jaundice. Some degree of hyperbilirubinemia is very common in babies correct after nascence, especially premies.
Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) leading to cognitive or motor disability or filibuster – Damage to cells in the fundamental nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) from inadequate oxygen. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy allegedly may cause in death in the newborn period or result in what is afterwards recognized equally developmental filibuster, mental retardation, or cerebral palsy.
Hypoglycemia – Low blood sugar (glucose). When symptoms of hypoglycemia occur together with a documented blood glucose under 45 mg/dl, and the symptoms promptly resolve with the assistants of glucose, the diagnosis of hypoglycemia can exist fabricated with some certainty.
Hypoglycemia is merely significant when it is associated with symptoms. The symptoms may include anxiety, sweating, tremor, palpitations, nausea, and pallor. Hypoglycemia likewise starves the encephalon of glucose energy, which is essential for proper brain part. Lack of glucose free energy to the brain can cause symptoms ranging from headache, balmy defoliation, and aberrant beliefs, to loss of consciousness, seizure, and coma. Severe hypoglycemia can cause decease.
Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH) – bleeding within or effectually the ventricles, the spaces in the brain containing the cerebral spinal fluid.
Necrotizing enterocolitis (severe abdominal inflammation) – a serious bacterial infection in the intestine, primarily of sick or premature newborn infants. Information technology can cause the death (necrosis) of intestinal tissue and progress to blood poisoning (septicemia). Information technology is a serious infection that tin produce complications in the intestine itself—such equally ulcers, perforations (holes) in the intestinal wall, and tissue necrosis—as well as progress to life-threatening septicemia. Necrotizing enterocolitis most unremarkably affects the lower portion of the small intestine (ileum). Information technology is less mutual in the colon and upper pocket-sized bowel.
Neonatal Sepsis – A serious claret bacterial infection in an babe less than 4 weeks of age. Babies with sepsis may exist listless, overly sleepy, floppy, weak, and very stake.
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) – Illness virtually usually seen in preemies when the tiny air sacs in the lungs plummet when the baby exhales. It is caused by a lack of lung surfactant.
Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) – a affliction that affects immature vasculature in the eyes of premature babies. It tin can exist balmy with no visual defects, or information technology may become aggressive with new blood vessel germination (neovascularization) and progress to retinal detachment and blindness. Every bit smaller and younger babies are surviving, the incidence of ROP has increased.
Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE) – a chronic inflammatory illness of unknown cause that affects multiple organ systems. Immunologic abnormalities, specially the product of a number of antinuclear antibodies, are another prominent feature of this disease.
References
1. Bradford, Due north. Your premature baby; the first five years. Firefly Books Ltd, Toronto, Ontario 2003.
2. Braner D., Kattwinkel J., Denson S., Zaichkin J.(2000) American Academy of Pediatrics. Special considerations. Textbook of Neonatal Resuscitation. fourth ed. Elk Grove Hamlet, IL: 2000: 7–nineteen
3. Deborah Due east. Campbell, MD; Sonia O. Imaizumi, Doc; Judy C. Bernbaum, Doc. Chapter 95: Health and Developmental Outcomes of Infants Requiring Neonatal Intensive Care. AAP Textbook of Pediatric Intendance, 2008.
4. Draper, E.S., Manktelow, B., Field, D.J., James, D. (1999). Prediction of survival for preterm births by weight and gestational age: retrospective population based study. BMJ, 319: 1093-1097
v. Evans, N. (1993) Diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus in the preterm newborn. Archives of disease in childhood: vol. 68 (1 Spec No.): 58-61.
6. Funai, E. Preterm Labour. Uptodate 2007.
seven. Halpern, Thou.D., Holubec, H., Dominguez, J.A., Meza, Y.G., Williams, C.S., Ruth, Chiliad.C., McCuskey, R.S., and Dvorak, B. (2003). Hepatic inflammatory mediators contribute to abdominal impairment in necrotizing enterocolitis. American Periodical of Physiology – Gastrointestinal Liver Physiology: 284: (iv)
eight. Hutchinson, A.Chiliad., Saunders, R.A., O'Neil, J.W., Lovering, A., Wilson, M.Eastward. (1998). Time of Initial Screening Examinations for Retinopathy of Prematurity. Archive of Opthamology: 116 (5): 608-612.
nine. Jones H.P, Karuri, S, Cronin, C.Grand, Ohlsson, A, Peliowski, A, Synnes, A, Lee, Southward.K. 2005. Actuarial Survival of a Large Canadian Cohort of Preterm Infants. Journal of BMC Pediatrics, five (40): 1-xiii
10. Lansdown, R, Walker, Grand. Your Child'southward Development from Nascence to Adolescence. Frances Lincoln Limited, 1996.
11. Lynn M. Iwamoto. Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and Residents Section of Pediatrics. University of Hawaii John A. Burns Schoolhouse of Medicine Chapter III.9. Neonatal Seizures
12. Milliken, J.C, D'Souza, G. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. Emedicine, 2007.
13. National Women'south Newborn Services Annual Clinical Report. The Auckland Commune Health Board, 2007.
14. Sears, W, Sears, R, Sears, J, Sears, M. (2004). The Premature Baby Book: Everything y'all need to know nigh your premature baby from nativity to age one. Little,Chocolate-brown and Company, New York, NY.
15. Simpkins, C.J. (2004). Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infections in Patients with Hydrocephalus. Pediatric Nursing: 31(6).
xvi. Swammy, G.K, Ostbye, T, Skjaerven, R. 2008. Clan of Preterm Birth with Long-term Survival, Reproduction, and Next-generation Preterm Birth. Journal of the American Medical Clan, 299 (12): 1429-1436
17. The Academy of Pennsylvania Health Systems. Intraventricular Hemmorage. 2009.
18. Verrees, Chiliad., Selman, W.R. (2004). Management of Normal Pressure level Hydrocephalus. American Family Physician: 70(half dozen).
19. Yates Jr., F.,D. (2008) Medical Decision Making for the Marginally Viable Infant. American Medical Clan Journal of Ethics: x (10): 673-676.
Acknowledgments
Written past: John Hilhorst
Edited by: Anne Marie Jekyll
Babies Categorized as Very Low Birth Weight Weigh Less Than _____ Pounds.
Source: https://learn.pediatrics.ubc.ca/body-systems/neonate/consequences-of-prematurity/